Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Suyama, Kenya; Ueki, Taro; Gunji, Satoshi; Watanabe, Tomoaki; Araki, Shohei; Fukuda, Kodai; Yamane, Yuichi; Izawa, Kazuhiko; Nagaya, Yasunobu; Kikuchi, Takeo; et al.
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2023/10
To remove and store safely the fuel debris generated by the severe accident of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station in 2011 is one of the most important and challenging topics for decommissioning of the damaged reactors in Fukushima. To validate the adopted method for the evaluation of criticality safety control of the fuel debris through comparison with the experimental data obtained by the criticality experiments, the Nuclear Regulation Authority (NRA) of Japan funds a research and development project which was entrusted to the Nuclear Safety Research Center (NSRC) of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) from 2014. In this project, JAEA has been conducting such activities as i) comprehensive computation of the criticality characteristics of the fuel debris and making database (criticality map of the fuel debris), ii) development of new continuous energy Monte Carlo code, iii) evaluation of criticality accident and iv) modification of the critical assembly STACY for the experiments for validation of criticality safety control methodology. After the last ICNC2019, the project has the substantial progress in the modification of STACY which will start officially operation from May 2024 and the development of the Monte Carlo Code "Solomon" suitable for the criticality calculation for materials having spatially random distribution complies with the power spectrum. We present the whole picture of this research and development project and status of each technical topics in the session.
Gunji, Satoshi; Yoshikawa, Tomoki; Araki, Shohei; Izawa, Kazuhiko; Suyama, Kenya
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2023/10
Since the compositions and properties of the fuel debris are uncertain, critical experiments are required to validate calculation codes and nuclear data used for the safety evaluation. For this purpose, JAEA has been modifying a critical assembly called "STACY". The first criticality of the new STACY is scheduled for spring 2024. This paper reports the consideration results of the core configurations of the new STACY at the first criticality. We prepared two sets of gird plates with different neutron moderation conditions (their intervals are 1.50 cm and 1.27 cm). However, there is a limitation on the number of available UO fuel rods. In addition, we would like to set the critical water heights for the first criticality at around 95 cm. This is to avoid the reactive effect of the aluminum alloy middle grid plates (Approx. 98 cm high). The core configurations for the first criticality satisfying these conditions were constructed by computational analysis. A square core configuration with the 1.50 cm grid plate that is close to the optimum moderation condition needs 261 fuel rods to reach criticality. As to the 1.27 cm grid plate, we considered two core configurations with 1.80 cm intervals by using a checkerboard arrangement. One of them has two regions core configuration with 1.27 and 1.80 cm intervals, and the other has only 1.80 cm intervals. They need 341 and 201 fuel rods for the criticality, respectively. This paper shows these three core configurations and their calculation models.
fuel rods. In addition, we would like to set the critical water heights for the first criticality at around 95 cm. This is to avoid the reactive effect of the aluminum alloy middle grid plates (Approx. 98 cm high). The core configurations for the first criticality satisfying these conditions were constructed by computational analysis. A square core configuration with the 1.50 cm grid plate that is close to the optimum moderation condition needs 261 fuel rods to reach criticality. As to the 1.27 cm grid plate, we considered two core configurations with 1.80 cm intervals by using a checkerboard arrangement. One of them has two regions core configuration with 1.27 and 1.80 cm intervals, and the other has only 1.80 cm intervals. They need 341 and 201 fuel rods for the criticality, respectively. This paper shows these three core configurations and their calculation models.
Gunji, Satoshi; Araki, Shohei; Arakaki, Yu; Izawa, Kazuhiko; Suyama, Kenya
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2023/10
JAEA has been modifying a critical assembly called STACY from a solution system to a light-water moderated heterogeneous system to validate computation results of criticality characteristics of fuel debris generated in the accident at TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. To experimentally simulate the composition and characteristics of fuel debris, we will prepare several grid plates which make particular neutron moderation conditions and a number of rod-shaped concrete and stainless-steel materials. Experiments to evaluate fuel debris's criticality characteristics are scheduled using these devices and materials. This series of STACY experiments are planned to measure the reactivity of fuel debris-simulated samples, measure the critical mass of core configurations containing structural materials such as concrete and stainless steels, and the change in critical mass when their arrangement becomes non-uniform. Furthermore, two divided cores experiments are scheduled that statically simulate fuel debris falling, and also scheduled that subcriticality measurement experiments with partially different neutron moderation conditions. The experimental plans have been considered taking into account some experimental constraints. This paper shows the schedule of these experiments, as well as the computation results of the optimized core configurations and expected results for each experiment.
Gunji, Satoshi; Araki, Shohei; Watanabe, Tomoaki; Fernex, F.*; Leclaire, N.*; Bardelay, A.*; Suyama, Kenya
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2023/10
Institut de radioprotection et de s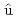 ret
ret nucl
nucl aire (IRSN) and Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) have a long-standing partnership in the field of criticality safety. In this collaboration, IRSN and JAEA are planning a joint experiment using the new STACY critical assembly, modified by JAEA. In order to compare the codes (MVP3, MORET6, etc.) and nuclear data (JENDL and JEFF) used by both institutes in the planning of the STACY experiment, benchmark calculations of the Apparatus B and TCA, which are critical assemblies once owned by both institutes, benchmarks from the ICSBEP handbook and the computational model of the new STACY were performed. Including the new STACY calculation model, the calculations include several different neutron moderation conditions and critical water heights. There were slight systematic differences in the calculation results, which may have originated from the processing and/or format of the nuclear data libraries. However, it was found that the calculated results, including the new codes and the new nuclear data, are in good agreement with the experimental values. Therefore, there are no issues to use them for the design of experiments for the new STACY. Furthermore, the impact of the new TSL data included in JENDL-5 on the effective multiplication factor was investigated. Experimental validation for them will be completed by critical experiments of the new STACY by both institutes.
aire (IRSN) and Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) have a long-standing partnership in the field of criticality safety. In this collaboration, IRSN and JAEA are planning a joint experiment using the new STACY critical assembly, modified by JAEA. In order to compare the codes (MVP3, MORET6, etc.) and nuclear data (JENDL and JEFF) used by both institutes in the planning of the STACY experiment, benchmark calculations of the Apparatus B and TCA, which are critical assemblies once owned by both institutes, benchmarks from the ICSBEP handbook and the computational model of the new STACY were performed. Including the new STACY calculation model, the calculations include several different neutron moderation conditions and critical water heights. There were slight systematic differences in the calculation results, which may have originated from the processing and/or format of the nuclear data libraries. However, it was found that the calculated results, including the new codes and the new nuclear data, are in good agreement with the experimental values. Therefore, there are no issues to use them for the design of experiments for the new STACY. Furthermore, the impact of the new TSL data included in JENDL-5 on the effective multiplication factor was investigated. Experimental validation for them will be completed by critical experiments of the new STACY by both institutes.
Araki, Shohei; Gunji, Satoshi; Arakaki, Yu; Yoshikawa, Tomoki; Murakami, Takahiko; Kobayashi, Fuyumi; Izawa, Kazuhiko; Suyama, Kenya
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2023/10
New experiments simulating fuel debris in the new criticality assembly, STACY, are designed to contribute to the validation of criticality calculations for criticality control of the fuel debris in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident. In the new STACY experiment, a two-region core consisting of a driver region and a test region was investigated in order to configure a debris-simulated core with under-moderation condition (lattice pitch 1.27-cm) having the constraint of available fuel rod number. The test region with a 1.27-cm lattice pitch is surrounded by the driver region, in which fuel rods are arranged in a checkerboard pattern on a 1.27-cm lattice plate, with a 1.80-cm lattice pitch. Neutron spectra and sensitivity were calculated by using MCNP6 and ENDF/B-VII. The core which has a 17 17 test region with 373 fuel rods is the largest two-region core under the constraint. It was found that the core which has a 17
17 test region with 373 fuel rods is the largest two-region core under the constraint. It was found that the core which has a 17 17 test region can simulate the neutron spectra of under-moderation condition in a 13
17 test region can simulate the neutron spectra of under-moderation condition in a 13 13 region inside the test region with the root-mean square percentage error of less than 5%. It was also confirmed that the sensitivity of
13 region inside the test region with the root-mean square percentage error of less than 5%. It was also confirmed that the sensitivity of  Si and
Si and  Ca (n,
Ca (n, ) reactions when the concrete simulant, was loaded could be simulated.
) reactions when the concrete simulant, was loaded could be simulated.
Araki, Shohei; Gunji, Satoshi; Arakaki, Yu; Murakami, Takahiko; Yoshikawa, Tomoki; Hasegawa, Kenta; Tada, Yuta; Izawa, Kazuhiko; Suyama, Kenya
Proceedings of 4th Reactor Physics Asia Conference (RPHA2023) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2023/10
To conduct integrated thermal power measurements for the performance test of the modified STACY, we re-analyzed the experimental data measured in the solution fuel STACY using the activation method. We validated its feasibility under the limited number of activation detectors. The re-analyzed results of the activation method by using MVP and PHITS with JENDL-4.0 indicated that the effect of the difference of the position between activation detectors was small enough, and the results agreed with that of the fission product analysis within almost 10%. It is conceivable that the activation method could be adopted instead of the fission product analysis.
 variations by nonuniform core configurations
variations by nonuniform core configurationsGunji, Satoshi; Araki, Shohei; Suyama, Kenya
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 197(8), p.2017 - 2029, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)The fuel debris generated by the accident at the Tokyo Electric Power Company's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant is expected to have not only heterogeneous but also nonuniform compositions. Similarly, damaged fuel assemblies remaining in the reactor vessels also have nonuniform configurations due to some missing fuel rods. This non-uniformity may cause changing neutron multiplication factors. The effect of non-uniformity on the neutron multiplication factor is clarified by computations, and the possibility of experimentally validating the computations used for criticality management is being investigated. For this purpose, in this study the criticality effects of several core configurations of a new critical assembly, STACY, of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency with nonuniform arrangements of uranium oxide fuel rods, concrete rods, and stainless-steel rods were studied to confirm benchmarking potential. The difference in these arrangements changed the neutron multiplication factor by more than 1 $. We confirmed that changes in local neutron moderation conditions and the clustering of specific components caused this effect. In addition, the feasibility of benchmark experimental cores with nonuniform arrangements is evaluated. If benchmarking of such experiments could be realized, it would help to validate calculation codes and to develop criticality management methods by machine learning.
Yokoyama, Kenji; Taninaka, Hiroshi
Kaku Deta Nyusu (Internet), (132), p.25 - 33, 2022/06
This article explains the results of integral test of JENDL-5 by benchmark analysis in fast reactor system, which were presented in a special session of the 2022 Spring Annual Meeting of the Atomic Energy Society of Japan (AESJ). The latest version of Japanese evaluated nuclear data library, JENDL-5, was released in December 2021. In order to confirm the applicability of JENDL-5 to the fast reactor system, we conducted a set of benchmark analysis using the integral experiment data included in the fast reactor nuclear design database which is being developed by JAEA. With respect to major nuclear characteristics in the standard fast reactor system, it was confirmed that the ratios of analysis result and experimental result (C/E values) based on JENDL-5 were almost the same as those of JENDL-4.0. In the special session, the results of sensitivity analysis were reported. Since the results have been described in the proceedings of the AESJ meeting, we add the results of the versions under development of JENDL-5 and discuss their relationship with the reported results of sensitivity analysis.
Fukaya, Yuji; Goto, Minoru; Nakagawa, Shigeaki; Nakajima, Kunihiro*; Takahashi, Kazuki*; Sakon, Atsushi*; Sano, Tadafumi*; Hashimoto, Kengo*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 247, p.09017_1 - 09017_8, 2021/02
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) started the Research and Development (R&D) to improve nuclear prediction techniques for High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactors (HTGRs). The objectives are to introduce a generalized bias factor method to avoid full mock-up experiment for the first commercial HTGR and to introduce reactor noise analysis to High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) experiment to observe subcriticality. To achieve the objectives, the reactor core of graphite-moderation system named B7/4"G2/8"p8EUNU+3/8"p38EU(1) was newly composed in the B-rack of Kyoto University Critical Assembly (KUCA). The core is composed of the fuel assembly, driver fuel assembly, graphite reflector, and polyethylene reflector. The fuel assembly is composed of enriched uranium plate, natural uranium plate and graphite plates to realize the average fuel enrichment of HTTR and it's spectrum. However, driver fuel assembly is necessary to achieve the criticality with the small-sized core. The core plays a role of the reference core of the bias factor method, and the reactor noise was measured to develop the noise analysis scheme. In this study, the overview of the criticality experiments is reported. The reactor configuration with graphite moderation system is rare case in the KUCA experiments, and this experiment is expected to contribute not only for an HTGR development but also for other types of a reactor in the graphite moderation system such as a molten salt reactor development.
Araki, Shohei; Gunji, Satoshi; Tonoike, Kotaro; Kobayashi, Fuyumi; Izawa, Kazuhiko; Ogawa, Kazuhiko
Proceedings of European Research Reactor Conference 2020 (RRFM 2020) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2020/10
Critical experiments of thermal neutron system are still expected to be playing an important role for wide technical issues. The Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) is renovating the Static Experimental Critical Facility (STACY) to maintain the experimental capability. The new STACY is designed as a general-purpose criticality facility. Its core mainly consists of low enriched UO fuel rods, grid plates, and light water moderator. The first experiment campaign in the new STACY aims to obtain criticality characteristics of fuel debris, which will be used in validation of criticality analysis methods. The designs of the experimental core configurations are in progress.
fuel rods, grid plates, and light water moderator. The first experiment campaign in the new STACY aims to obtain criticality characteristics of fuel debris, which will be used in validation of criticality analysis methods. The designs of the experimental core configurations are in progress.
Izawa, Kazuhiko; Ishii, Junichi; Okubo, Takuya; Ogawa, Kazuhiko; Tonoike, Kotaro
Proceedings of 11th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC 2019) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2019/09
Japan Atomic Energy Agency, JAEA, is conducting the renewal program of the heterogeneous water moderated critical assembly STACY (Static Experiment Critical Facility) in order to verify the criticality calculation considering fuel debris which have been produced in the accident of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. The first criticality of the new STACY is scheduled at the beginning of 2021. After the first criticality, it is necessary to perform a series of critical experiments with a series of basic experimental core in order to gain a proficiency of operators and grasp the uncertainty that accompanies the result of critical experiments in STACY. Prior to the construction of the new STACY, a series of neutronic calculation was carried out for licensing and planning first series of critical experiment. In this paper, possible core configuration of the basic experimental core and their limitations are discussed and presented.
Gunji, Satoshi; Clavel, J.-B.*; Tonoike, Kotaro; Duhamel, I.*
Proceedings of 11th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC 2019) (Internet), 11 Pages, 2019/09
The new criticality experiments facility STACY will be able to contribute to the validation of criticality calculations related to the fuel debris. The experimental core design is in progress in the frame of JAEA/IRSN collaboration. This paper presents the method applied to optimize the design of core configurations of the new STACY to measure the criticality characteristics of pseudo fuel debris focused on Molten Core Concrete Interaction (MCCI) debris. To ensure that a core configuration is relevant for code validation, it is important to evaluate the reactivity worth of the main isotopes and the keff sensitivity to their cross sections. To obtain maximum sensitivity of  Si capture reaction, some parameters of the core configuration, as for example the lattice pitch or the core dimensions, were adjusted using optimization algorithm to research efficiently the optimal core configurations.
Si capture reaction, some parameters of the core configuration, as for example the lattice pitch or the core dimensions, were adjusted using optimization algorithm to research efficiently the optimal core configurations.
Fukaya, Yuji; Nakagawa, Shigeaki; Goto, Minoru; Ishitsuka, Etsuo; Kawakami, Satoru; Uesaka, Takahiro; Morita, Keisuke; Sano, Tadafumi*
KURNS Progress Report 2018, P. 148, 2019/08
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) started the Research and Development (R&D) to improve nuclear prediction techniques for High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactors (HTGRs). The objectives are to introduce generalized bias factor method to avoid full mock-up experiment for the first commercial HTGR and to introduce reactor noise analysis to High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) experiment. To achieve the objectives, the reactor core of graphite moderation system named B7/4"G2/8"p8EUNU+3/8"p38EU(1) was newly composed in the B-rack of Kyoto University Critical Assembly (KUCA). The core plays a role of the reference core of the bias factor method, and the reactor noise was measured to develop the noise analysis scheme. In addition, training of operator of HTTR was also performed during the experiments.
Yokoyama, Kenji; Sugino, Kazuteru; Ishikawa, Makoto; Maruyama, Shuhei; Nagaya, Yasunobu; Numata, Kazuyuki*; Jin, Tomoyuki*
JAEA-Research 2018-011, 556 Pages, 2019/03
We have developed a new unified cross-section set ADJ2017, which is an improved version of the unified cross-section set ADJ2010 for fast reactors. The unified cross-section set is used for reflecting information of C/E values (analysis / experiment values) obtained by integral experiment analyses; the values are stored in the standard database for FBR core design via the cross-section adjustment methodology, which integrates with the information such as uncertainty (covariance) of nuclear data, uncertainty of integral experiment / analysis, sensitivity of integral experiment with respect to nuclear data. The ADJ2017 is based on Japan's latest nuclear data library JENDL-4.0 as in the previous version of ADJ2010, and it incorporates more information on integral experimental data sets related to minor actinides (MAs) and degraded plutonium (Pu). In the creation of ADJ2010, a total of 643 integral experimental data sets were analyzed and evaluated, and 488 of the integral experimental data sets were finally selected to be used for the cross-section adjustment. In contrast, we have evaluated a total of 719 data sets, and eventually adopted 620 integral experimental data sets to create ADJ2017. ADJ2017 shows almost the same performance as ADJ2010 for the main neutronic characteristics of conventional sodium-cooled MOX-fuel fast reactors. In addition, for the neutronic characteristics related to MA and degraded Pu, ADJ2017 improves the C/E values of the integral experimental data sets, and reduces the uncertainty induced by the nuclear data. ADJ2017 is expected to be widely used in the analysis and design research of fast reactors. Moreover, it is expected that the integral experimental data sets used for ADJ2017 can be utilized as a standard database of FBR core design.
Tsujimura, Norio; Yoshida, Tadayoshi; Sanada, Yukihisa
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 24, p.011013_1 - 011013_6, 2019/01
Gunji, Satoshi; Tonoike, Kotaro; Izawa, Kazuhiko; Sono, Hiroki
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 101(Part C), p.321 - 328, 2017/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:28.82(Nuclear Science & Technology)Criticality safety of fuel debris, particularly MCCI (Molten-Core-Concrete-Interaction) products, is one of the major safety issues for decommissioning of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. Criticality or subcriticality condition of the fuel debris is still uncertain; its composition, location, neutron moderation, etc. are not yet confirmed. The effectiveness of neutron poison in cooling water is also uncertain for use as a criticality control of fuel debris. A database of computational models is being built by Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), covering a wide range of possible conditions of such composition, neutron moderation, etc., to facilitate assessing criticality characteristics once fuel debris samples are taken and their conditions are known. The computational models also include uncertainties which are to be clarified by critical experiments. These experiments are planned and will be conducted by JAEA with the modified STACY (STAtic experiment Critical facilitY) and samples to simulate fuel debris compositions. Each of the samples will be cladded by a zircalloy tube whose outer shape is compatible with the fuel rod of STACY and loaded into an array of the fuel rods. This report introduces a study of experimental core configurations to measure the reactivity worth of samples simulating MCCI products. Parameters to be varied in the computation models for the experimental series are:(1) Uranium dioxide with  U enrichments of 3, 4, and 5 wt.%; (2) Concrete volume fraction in the samples of 0, 20, 40, 60, and 80%; and (3) Porosity of the samples filled from 0 to 80% where the sample void is filled with water. It is concluded that the measurement is feasible in both under- and over-moderated conditions. Additionally, the required amount of samples was estimated.
U enrichments of 3, 4, and 5 wt.%; (2) Concrete volume fraction in the samples of 0, 20, 40, 60, and 80%; and (3) Porosity of the samples filled from 0 to 80% where the sample void is filled with water. It is concluded that the measurement is feasible in both under- and over-moderated conditions. Additionally, the required amount of samples was estimated.
Uesaka, Mitsuru*; Mineo, Hideaki
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 58(8), p.468 - 473, 2016/08
, 58(8), p.468 - 473, 2016/08
All the research reactors and critical assemblies (hereinafter RRCAs) in Japan are stopped in order to fulfil the new regulatory requirements, which were reinforced after the accident at the Tokyo Electric Power Company's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. These RRCAs have played important roles in the areas of human resource development, academic research, medical and industrial application of nuclear technology. Prolonged stoppage of RRCAs affects adversely those activities. Atomic Energy Society of Japan set up a group to discuss this issue. The group has shown a proposal that the roles of the RRCAs, which are indispensable facilities to nuclear human resource development, should be placed positively in the energy policy and the science and technology policy of the country.
 Np using variable neutron field at KURRI-LINAC
Np using variable neutron field at KURRI-LINACTakahashi, Yoshiyuki*; Hori, Junichi*; Sano, Tadafumi*; Yagi, Takahiro*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Pyeon, C. H.*; Nakamura, Shoji; Harada, Hideo
Proceedings of International Conference on the Physics of Reactors; Unifying Theory and Experiments in the 21st Century (PHYSOR 2016) (USB Flash Drive), p.645 - 652, 2016/05
For the reduction of radioactive toxicities, feasibility study of nuclear transmutation of minor actinides (MAs) and long-lived fission products (LLFPs) by utilizing innovative nuclear reactor system (i.e. fast breeder reactors and accelerator-driven systems) has been actively conducted. To design these nuclear reactor systems, the accurate nuclear data are required. Therefore, to obtain more accurate nuclear data, the project entitled as "Research and development for Accuracy Improvement of neutron nuclear data on Minor ACtinides(AIMAC)" has been started as one of the "Innovative Nuclear Research and Development Program". In a part of this project, the nuclear data of MAs are verified in the variable neutron spectra field at Kyoto University Research Reactor Institute-LINear ACcelerator (KURRI-LINAC) and Kyoto University Critical Assembly (KUCA). And the differential TOF data is cross-checked with an integral data for the validation of  Np,
Np,  Am, and
Am, and  Am. In this summary, the results of reaction rate of neutron capture cross section of
Am. In this summary, the results of reaction rate of neutron capture cross section of  Np are reported as an example in the study.
Np are reported as an example in the study.
Gunji, Satoshi; Tonoike, Kotaro; Izawa, Kazuhiko; Sono, Hiroki
Proceedings of International Conference on the Physics of Reactors; Unifying Theory and Experiments in the 21st Century (PHYSOR 2016) (USB Flash Drive), p.3927 - 3936, 2016/05
Criticality safety of fuel debris including MCCI products is one of the major safety is-sues for decommissioning of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. Criticality or subcriticality condition of the fuel debris is still uncertain since its composition, location, neutron moderation, etc. are not confirmed. Also uncertain in criticality control of fuel debris is the effectiveness of neutron poison in cooling water. A database is being built by computation in JAEA, covering a wide range of possible conditions of such composition, neutron moderation, etc., to facilitate assessing criticality characteristics when fuel debris samples are taken and their conditions are known. The computation also has uncertainties to be clarified by critical experiments, which is planned by JAEA to be conducted with the modified STACY and samples simulating fuel debris compositions. This report introduces a study of experimental core configurations for reactivity worth measurements of samples simulating MCCI products. It is concluded that the measurement is feasible in both under- and over-moderated conditions. Additionally, required amount of samples was estimated.
Izawa, Kazuhiko; Tonoike, Kotaro; Leclaire, N.*; Duhamel, I.*
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC 2015) (DVD-ROM), p.965 - 976, 2015/09
In the post-Fukushima prospect, Japan Atomic Energy Agency, JAEA, intends to re-open its Static Experiment Critical Facility STACY, in order to contribute to the validation of fuel debris calculations in conditions close to those affected by the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station accident. The reactor core of STACY is being modified by JAEA from homogeneous solution fuel core to heterogeneous pin-type fuel core. The first step of critical experiments is to establish reference experiments involving lattices of UO rods without fuel debris. A design of such experiments is in progress for the widest range of moderation ratios in the frame of JAEA/IRSN collaboration. For that purpose, perturbation calculation technique and stochastic geometry modeling technique were used with the MCNP5 and the JENDL-4.0 evaluated nuclear data library. The proposed paper will discuss all the aforementioned issues.
rods without fuel debris. A design of such experiments is in progress for the widest range of moderation ratios in the frame of JAEA/IRSN collaboration. For that purpose, perturbation calculation technique and stochastic geometry modeling technique were used with the MCNP5 and the JENDL-4.0 evaluated nuclear data library. The proposed paper will discuss all the aforementioned issues.